Encode N ary Tree to Binary Tree
This page explains Java solution to problem Encode N ary Tree to Binary Tree using Tree data structure.
Problem Statement
Design an algorithm to encode an N-ary tree into a binary tree and decode the binary tree to get the original N-ary tree.
An N-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than N children. Similarly, a binary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than 2 children.
There is no restriction on how your encode/decode algorithm should work.
Example 1: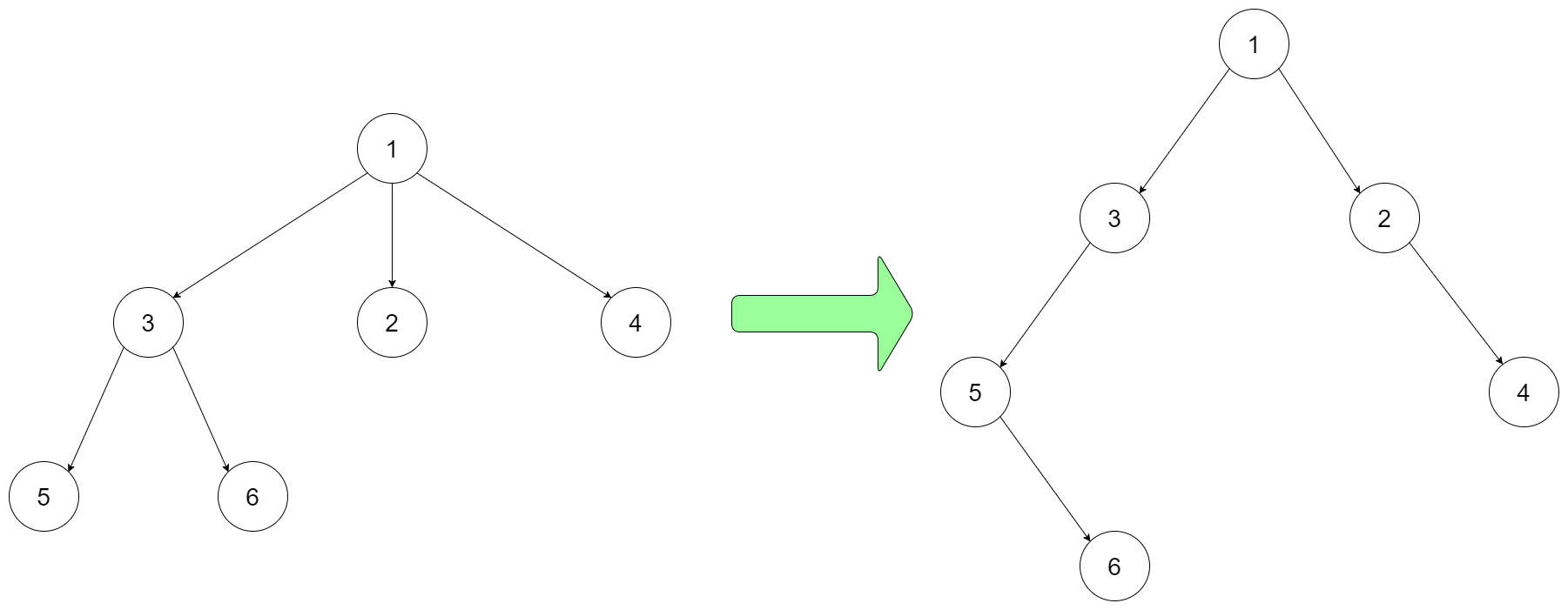
Solution
If you have any suggestions in below code, please create a pull request by clicking here.
package com.vc.hard;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class EncodeNAryTreeToBinaryTree {
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
public TreeNode encode(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
else {
TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(root.val);
if(root.children != null && root.children.size() > 0) {
tree.left = encode(root.children.get(0));
TreeNode current = tree.left;
for(int i = 1; i < root.children.size(); i++) {
current.right = encode(root.children.get(i));
current = current.right;
}
}
return tree;
}
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
public Node decode(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
else {
Node node = new Node(root.val, new ArrayList<>());
TreeNode current = root.left;
while(current != null) {
node.children.add(decode(current));
current = current.right;
}
return node;
}
}
}
Time Complexity
O(N) Where
N is total number of elements in an input tree
Space Complexity
O(1)